Natural Language Processing with Disaster Tweets
(based on this project)
Objective: Predict which Tweets are about real disasters and which ones are not
Setup
Install necessary data/libraries
!pip install pyspellchecker &> /dev/null
!pip install contractions &> /dev/null
!pip install num2words &> /dev/null
!pip install emoji &> /dev/null
!pip install textacy &> /dev/null
!pip install nltk &> /dev/null
Setup
# data science
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# plotting
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from wordcloud import WordCloud
from yellowbrick.text import TSNEVisualizer
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
sns.set_context("notebook", rc={"font.size":16,
"axes.titlesize":20,
"axes.labelsize":18})
# nlp
import re
import string
from collections import Counter
from spellchecker import SpellChecker
import contractions
from num2words import num2words
import emoji
import random
from textacy import extract
# nltk
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer, PorterStemmer
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
nltk.download('stopwords')
nltk.download('wordnet')
nltk.download('punkt')
nltk.download('wordnet')
nltk.download('averaged_perceptron_tagger')
nltk.download('punkt')
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer
from yellowbrick.text.freqdist import FreqDistVisualizer
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
# misc
# progress bar
from tqdm import tqdm
tqdm.pandas()
# color outputs
from termcolor import colored
# warnings
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# Typing
from typing import List, Tuple
# !python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm
A note on the libraries being used:
For the actual program:
- spellchecker: pure python spell checking using the levenshtein
- contractions: fixes contractions such as “you’re” to “you are”
- num2words: convert numbers to words. 42 –> forty-two
- emoji: python emojis
- textacy: python library for NLP tasks built on spaCy
- nltk: leading platform for building python programs to work with human language data
For visualization:
- yellowbrick: machine learning visualization
- gensim: topic modelling for Humans, vector embedding
- tqdm: fast, extendible progress bar
- termcolor: color formatting for output
Text Cleanup and Preprocessing
Convert to lowercase
Creating function to convert text to lowercase
def lower_case(text: str) -> str:
return text.lower()
Remove whitespace, linebreaks, and tabs
def remove_spaces_tabs(text: str) -> str:
return " ".join(text.split())
Get rid of punctuation
def remove_punct(text: str) -> str:
translator = str.maketrans("", "", string.punctuation)
return text.translate(translator)
Remove single characters
def remove_single_char(text: str) -> str:
return re.sub(r"\b[a-zA-Z]\b", "", text)
Remove html formatting
def remove_html(text: str) -> str:
html = re.compile(r"<.*?>")
return html.sub(r"", text)
Remove URL
def remove_url(text: str) -> str:
url = re.compile(r"https?://\S+|www\.\S+")
return url.sub(r"", text)
Removing Emojis
def remove_emoji(text: str) -> str:
# Reference : https://gist.github.com/slowkow/7a7f61f495e3dbb7e3d767f97bd7304b
emoji_pattern = re.compile(
"["
"\U0001F600-\U0001F64F" # emoticons
"\U0001F300-\U0001F5FF" # symbols & pictographs
"\U0001F680-\U0001F6FF" # transport & map symbols
"\U0001F1E0-\U0001F1FF" # flags (iOS)
"]+",
flags=re.UNICODE,
)
return emoji_pattern.sub(r"", text)
Remove Stopwords
Stopwords are common words in text that are not significant.
def remove_stopwords(text: str) -> str:
stop_words = set(stopwords.words("english"))
stop_words.update(["time"]) # add custom stopwords
stop_words -= {"no", "not"} # remove custom stopwords
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
filtered_sentence = [w for w in word_tokens if not w in stop_words]
return " ".join(filtered_sentence)
Convert emojis to text
def emoji2word(text: str) -> str:
return " ".join([emoji.demojize(w) if w in emoji.EMOJI_DATA else w for w in text.split()])
Convert digits to words
def convert_digits_to_words(text: str) -> str:
return " ".join([num2words(w) if w.isdigit() else w for w in text.split()])
Update and expand contractions
def expand_contractions(text: str) -> str:
return contractions.fix(text)
Lemmatization
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
def lemmatize_text_custom(text: str, lemmatizer) -> str:
wordnet_map = {
"J": wordnet.ADJ,
"N": wordnet.NOUN,
"V": wordnet.VERB,
"R": wordnet.ADV,
}
w_pos_tags = nltk.pos_tag(text.split())
lemmatized_output = " ".join([lemmatizer.lemmatize(w, wordnet_map.get(pos[0], wordnet.NOUN)) for w, pos in w_pos_tags])
return lemmatized_output
Stemming
Reducing the words to only the word stems.
def stem_text_custom(text: str, stemmer) -> str:
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
stemmed_output = " ".join([stemmer.stem(w) for w in word_tokens])
return stemmed_output
Spell Check
Finally, we spell check the test for better data.
def correct_spelling(text: str) -> str:
spell = SpellChecker()
corrected_text = []
misspelled_words = spell.unknown(text.split())
for word in text.split():
if word in misspelled_words:
# if correction is none return the original word
if spell.correction(word) is not None:
corrected_text.append(spell.correction(word))
else:
corrected_text.append(word)
else:
corrected_text.append(word)
return " ".join(corrected_text)
Reading the Data
url_train = 'https://drive.google.com/file/d/16r3kpP6Z6Jpeb6TLXYAS_asj6YUyh575/view?usp=sharing'
url_test = 'https://drive.google.com/file/d/1TkOWOFK-XiIHBytAlkbFKQoh_Yb9tVFj/view?usp=sharing'
path = 'https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id='+url_train.split('/')[-2]
df_train = pd.read_csv(path)
path = 'https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id='+url_test.split('/')[-2]
df_test = pd.read_csv(path)
print('train shape = {}'.format(df_train.shape))
print('train memory = {:.3f} MB'.format(df_train.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2))
print('Test shape = {}'.format(df_test.shape))
print('Test memory = {:.3f} MB'.format(df_test.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2))
train shape = (7613, 5)
train memory = 0.291 MB
Test shape = (3263, 4)
Test memory = 0.100 MB
df_train.head()
| id | keyword | location | text | target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NaN | NaN | Our Deeds are the Reason of this #earthquake M… | 1 |
| 4 | NaN | NaN | Forest fire near La Ronge Sask. Canada | 1 |
| 5 | NaN | NaN | All residents asked to ‘shelter in place’ are … | 1 |
| 6 | NaN | NaN | 13,000 people receive #wildfires evacuation or… | 1 |
| 7 | NaN | NaN | Just got sent this photo from Ruby #Alaska as … | 1 |
target:’1’ indicates a real disaster and ‘0’ indicates a not real disaster
text: the text of the tweet
location: where the tweet orginated
keyword: a particular keyword from the tweet (may be blank)
id: unique id given to each tweet
Text Preprocessing
Creating a text cleaning pipeline using the functions we just made.
pipeline = [
lower_case,
expand_contractions,
remove_spaces_tabs,
remove_url,
remove_punct,
remove_single_char,
remove_html,
remove_stopwords,
# other functions...
]
def prepare(text, pipeline, lemmatizer=None, stemmer=None):
tokens = text
for transform in pipeline:
# if lemmatize or stem function pass in, perform transformation
if transform.__name__ == "lemmatize_text_custom":
tokens = transform(tokens, lemmatizer)
elif transform.__name__ == "stem_text_custom":
tokens = transform(tokens, stemmer)
else:
tokens = transform(tokens)
return tokens
df_train["clean_text"] = df_train["text"].progress_apply(prepare, pipeline=pipeline)
df_test["clean_text"] = df_test["text"].progress_apply(prepare, pipeline=pipeline)
Data Visualizations
n-grams
def get_top_ngrams(text: pd.Series, ngram: int =1, top_n: int =10) -> List[Tuple[str, int]]:
vec = CountVectorizer(ngram_range=(ngram, ngram), stop_words="english").fit(text)
bag_of_words = vec.transform(text)
sum_words = bag_of_words.sum(axis=0)
words_freq = [(word, sum_words[0, idx]) for word, idx in vec.vocabulary_.items()]
words_freq = sorted(words_freq, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return words_freq[:top_n]
unigrams
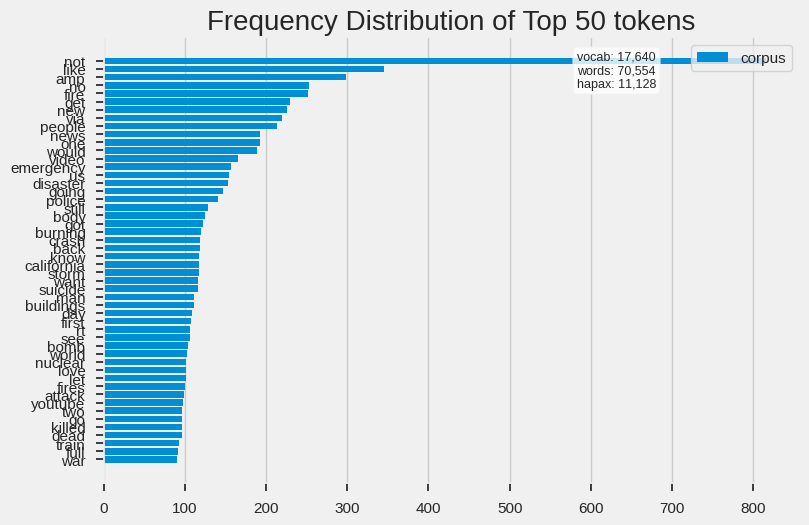
get_top_ngrams(df_train["clean_text"])
[('like', 345),
('amp', 298),
('new', 226),
('people', 213),
('news', 193),
('video', 165),
('emergency', 157),
('disaster', 153),
('going', 147),
('police', 141)]
def plot_freq_dist(text: pd.Series) -> None:
vectorizer = CountVectorizer()
docs = vectorizer.fit_transform(text)
features = vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
visualizer = FreqDistVisualizer(features=features)
visualizer.fit(docs)
visualizer.poof();
plot_freq_dist(df_train["clean_text"])
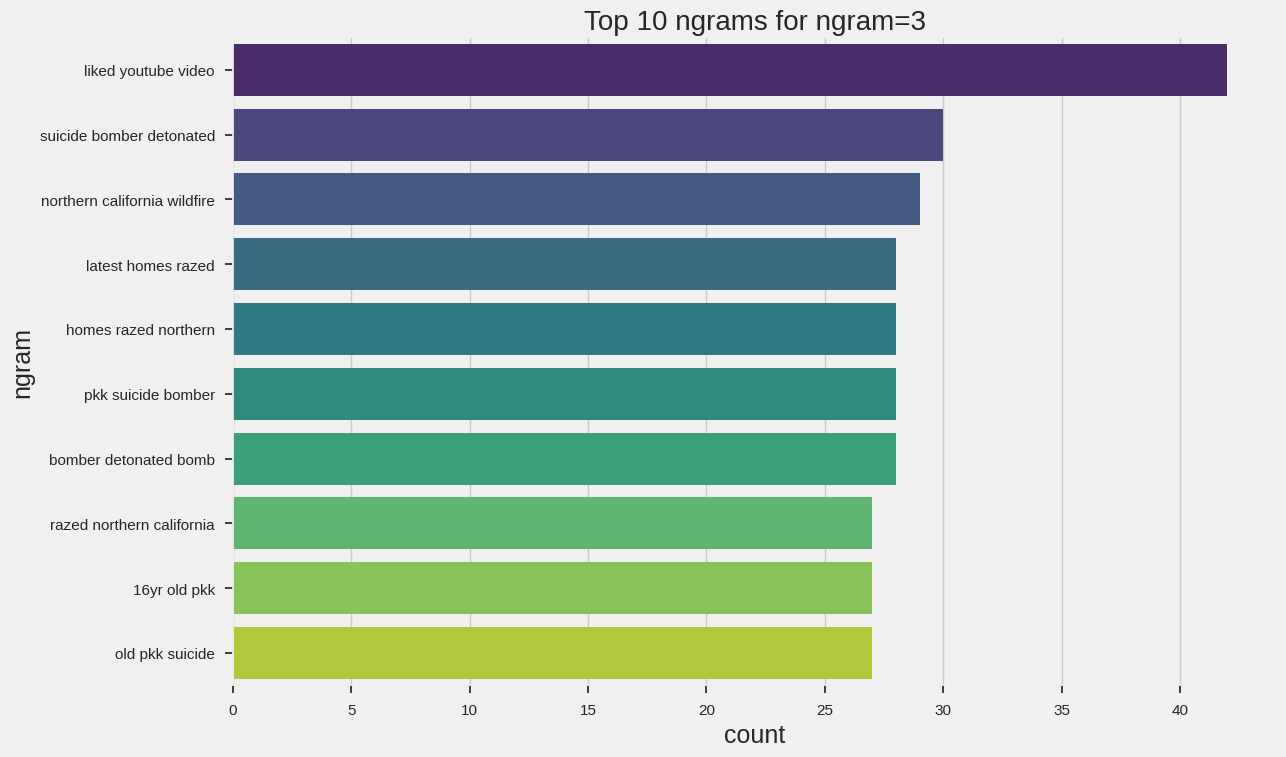
Trigram
get_top_ngrams(df_train["clean_text"],3)
[('liked youtube video', 42),
('suicide bomber detonated', 30),
('northern california wildfire', 29),
('latest homes razed', 28),
('homes razed northern', 28),
('pkk suicide bomber', 28),
('bomber detonated bomb', 28),
('razed northern california', 27),
('16yr old pkk', 27),
('old pkk suicide', 27)]
def plot_ngrams_bar(text: pd.Series, ngram: int =1, top_n: int =10) -> None:
ngrams = get_top_ngrams(text, ngram, top_n)
df_ngrams = pd.DataFrame(ngrams, columns=["ngram", "count"])
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.barplot(x="count", y="ngram", data=df_ngrams, palette="viridis")
plt.title(f"Top {top_n} ngrams for ngram={ngram}")
plt.show()
plot_ngrams_bar(df_train["clean_text"], ngram=3)
From here, we can use deep learning models to predict for the target. For that look here.