What is AI/ML?
Before we delve into Python, Numpy, and ultimately the fundamentals of AI/ML. You should know the difference between AI and ML:
AI: making machines capable of “intelligent” behavior (broad-concept) AI is a vast area of study; we will be mostly focusing on ML ML: subset of AI, algorithms making decisions through patterns from data (method)
In other words,
Ever wish your computer could be more like a savvy sidekick than a clueless sidekick? AI is the brainiac dreaming of understanding your vibes, and ML is its secret sauce – the tech making your computer less ‘I follow orders’ and more ‘I’ve got this, boss!’ It’s the reason your tech is getting sassier and smarter.
In order to start using AI/ML, Data is crucial! Quality of data IMPACT model performance and decision-making. From training to evaluation, data plays a central role in building reliable and effective AI systems.
Types of AI
Cognitive Modeling - study in computer science that studies and attempts to simulate how humans think
John McCarthy - “Every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it.”
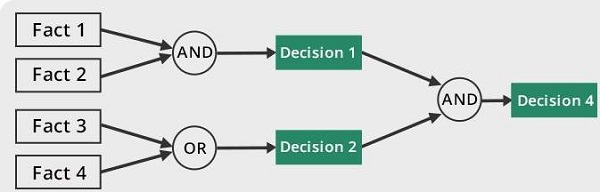
Good Old Fashioned AI (Symbolic)
- Rule-based AI
- Machine performs explicit instructions (IF-THEN) (Expert systems)
- Programmers give rules, instructions, and facts to perform pattern matching
- Logic and search
New Fangled AI (Connectionist)
- Machine Learning
- Machines must learn instructions through training
- The network discovers the rules from training data.
- Applies statistical regression models to adjust the weight coefficients of their intermediate variables, until the best fitting model is found
- Needs large amounts of collected data for most applications
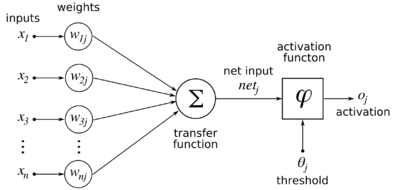
In this course, we will focus on Connectionist AI.